#HEALTHTALK 23: What you need to know about leukemia
Leukaemia is a German word originated from the combination of two Greek words 'leukos' meaning white and 'Haimas' meaning blood.
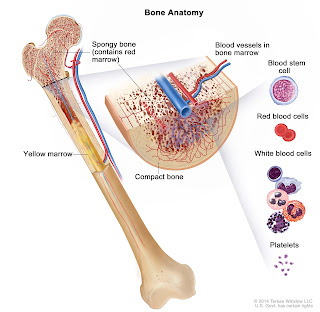
Leukaemia occurs when the bone marrow produces more than the required amount of white blood cells.
According to the dictionary, it is defined as a type of cancer of the bone marrow in which there is an excessive production of white blood cells.
Leukaemia is the most common malignant cancer in children, and affects older people too. But more chances of cure is predominant in children.
Leukaemia as a group of cancer cells usually begins in the bone marrow and forms abnormal cells known as leukaemia cells.
Leukemias and lymphomas are both known to belong to a broader group of tumors that affect the blood, bone marrow, and lymphoid system known as tumors of the hematopoietic and lymphoid tissues.
Leukemia Types
There are four major types of leukaemia and they are categorized according to acute and chronic, and subdivided into which kind of blood cells they affect. In general, They are as listed below:
• Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL): This is the most common type in children. It affects adults older than 64. In children, it is easily cured through chemotherapy and radiotherapy, but adults find it hard to survive it.
• Acute myeloid leukemia (AML): Common in adults than children, and is cured through chemotherapy. One thing about this type is that it happens more in adult males than females.
• Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL): This type is incurable. It affects older adults of 55 years and above, and mildly affects younger adults, but is very rare in children.
• Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML): Occurs more in adults but is rare in children.
Notwithstanding, there are a number of less common types such as hairy cell leukemia, known to be incurable but treatable; adult T-cell leukemia, large granular lymphocytic leukemia, T-cell prolymphocytic leukemia, etc.
Causes
The two major causes are: Genetic and environmental. Yet, there are some with untraceable causes.
Symptoms
In children, they commonly experience pale skin, enlarged spleen or liver, fever and easy bruising.
However, general symptoms of leukaemia include: weight loss, muscular weakness, pain in the joints, easy shortness of breath, fever, night sweats, easy bruising, frequent infections, loss of appetite, fatigue, seizures, etc.
Treatment
The most common treatment for leukaemia are: bone marrow transplant, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, gene therapy, stem cell transplant and supportive care.
Are there risk factors to leukaemia?
A lot of factors can lead to leukaemia. Examples are:
• Family history
• Downs syndrome
• Ionizing radiation
• Smoking
• Exposure to some chemicals
• Prior chemotherapy
Lilian Uchechi Eze is a Nutritionist-Dietitian and teacher in Lagos, Nigeria. She is also a Lead Content Creator at The Paul Anunaso Blog, and can be reached at lilian.thepaulanunasoblog@gmail.com
Disclaimer: The #HealthTalk series is aimed at informing the public in a general sense that is not necessarily professional. Hence, the information provided herein is not meant to replace the appropriate medical guidance of a trained and licensed physician. Doctor's counsels are to be taken in preference.
~ The Paul Anunaso Blog Team




Comments
Post a Comment